Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India, filing GST returns is a crucial compliance requirement for all registered taxpayers. In addition to guaranteeing seamless business operations, submitting the accurate return form by the deadline also helps prevent fines and interest. Knowing the many GST return types, forms, and dates is essential whether you’re a regular taxpayer, composition dealer, e-commerce operator, or non-resident taxable person.
Every GST return, from GSTR-1 to GSTR-9C, is broken down in this comprehensive guide, along with the deadlines, goals, frequency of filing, and penalties for late filing. With this streamlined explanation of all GST return requirements, you can stay educated and in compliance.
What Are GST Returns?
A GST return is a document filed by registered taxpayers to report their sales, purchases, tax collected, and tax paid. These returns enable the government to assess tax liabilities and ensure compliance.
Filing your GST returns on time is essential for staying compliant and avoiding penalties. Here’s a complete and easy-to-understand breakdown of all GST returns, including auto-generated forms like GSTR-2A, 2B, and more!

Why Filing of GST returns is important?
The importance of filing GST returns is several, including
For the Return Filer
- Required to comply with legal requirements
- helps in accurately determining personal and other people’s tax obligations.
- A tool for ITC claims
For the Government
- Source for obtaining Organizational Financial Statistics
- Examine the pertinent examples with effectiveness and efficiency.
- A foundation for future policy making
- helps in the creation of upcoming compliance protocols
- Evasions can be monitored more effectively.
- An efficient way to get information from taxpayers
Who Should you File GST Returns?
Based on their turnover, taxpayers are categorized under the GST Act. The GSTR filing requirements for the following companies are listed below:
- Companies that make more than ₹5 crore a year (or who do not choose the QRMP plan) must file two monthly returns and one yearly return, for a total of 25 returns annually.
- The QRMP program allows businesses with a yearly turnover of up to ₹5 crore to file nine returns, four GSTR-1, four GSTR-3B, and one annual return. Even when returns can be submitted on a quarterly basis, they are still required to pay taxes on a monthly basis.
- The filing method for composition dealers is different; they submit one GSTR-4 yearly return, four CMP-08 statements (quarterly tax payments), and five submissions annually.
Various Types of GST Returns
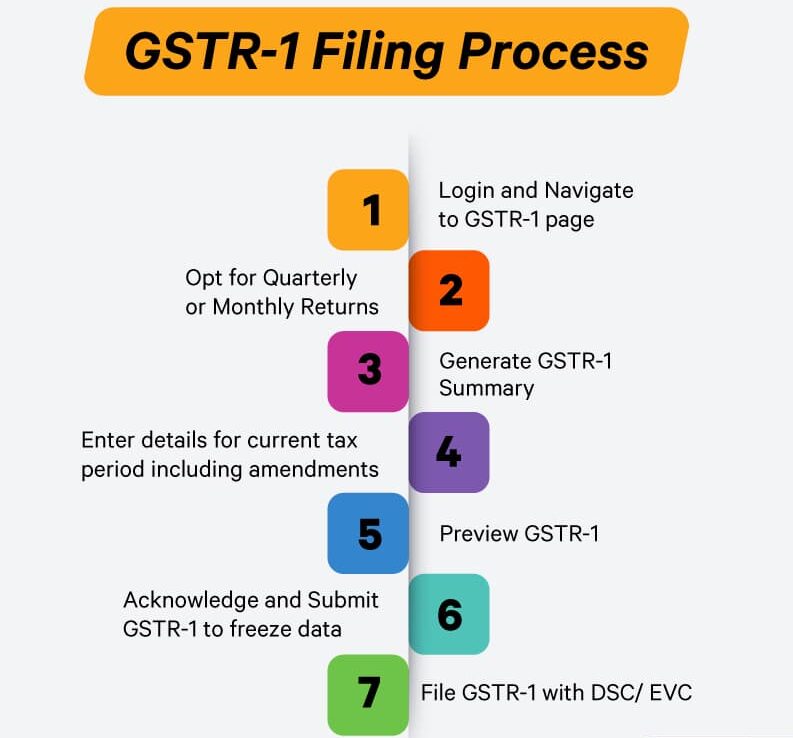
1. GSTR-1 – Outward Sales Details
- 🧑💼 Filed By: Regular registered taxpayers
- 📄 Contains: Invoice-wise details of outward (sales) supplies
- 📅 Due Date:
- Monthly: 11th of next month
- Quarterly (QRMP): 13th of month after quarter
- ✅ Purpose: Enables buyers to claim accurate ITC
2. GSTR-3B – Summary Return & Tax Payment
- 🧑💼 Filed By: All regular taxpayers
- 📄 Contains: Summary of sales, ITC, and tax paid
- 📅 Due Date:
- Monthly: 20th of next month
- QRMP: 22nd/24th of next month (based on state)
- ✅ Purpose: To discharge monthly/quarterly tax liability
3. GSTR-4 – Annual Return for Composition Dealers
- 👨🔧 Filed By: Composition scheme taxpayers
- 📄 Contains: Annual summary of sales, purchases, taxes
- 📅 Due Date: 30th April of the next financial year
- ✅ Purpose: Year-end return for composition taxpayers
4. CMP-08 – Quarterly Return for Composition Scheme
- 👨🔧 Filed By: Composition taxpayers
- 📄 Contains: Turnover and tax payable summary
- 📅 Due Date: 18th of the month after each quarter
- ✅ Purpose: Simple quarterly return for tax payment
5. GSTR-5 – Non-Resident Taxpayer Return
- 🌐 Filed By: Non-resident taxable persons
- 📄 Contains: Details of inward and outward supplies
- 📅 Due Date: 20th of next month
- ✅ Purpose: Tax compliance for non-residents doing business in India
6. GSTR-6 – Input Service Distributor (ISD) Return
- 🏢 Filed By: Input Service Distributors
- 📄 Contains: ITC received and distributed
- 📅 Due Date: 13th of next month
- ✅ Purpose: Distribution of ITC among different branches
7. GSTR-7 – TDS Return under GST
- 🏛️ Filed By: TDS deductors (Govt depts, notified entities)
- 📄 Contains: Tax deducted and paid
- 📅 Due Date: 10th of next month
- ✅ Purpose: Reporting and payment of GST TDS
8. GSTR-8 – TCS Return by E-commerce Operators
- 🛍️ Filed By: E-commerce platforms like Amazon, Flipkart
- 📄 Contains: TCS collected from sellers
- 📅 Due Date: 10th of next month
- ✅ Purpose: Report and pay tax collected at source
9. GSTR-9 – Annual Return for Regular Taxpayers
- 🧾 Filed By: Taxpayers with turnover > ₹2 Cr
- 📄 Contains: Yearly summary of sales, ITC, tax paid
- 📅 Due Date: 31st Dec of the next financial year
- ✅ Purpose: Annual compliance report
10. GSTR-9C – Reconciliation Statement & Audit
- 🧑💼 Filed By: Taxpayers with turnover > ₹5 Cr
- 📄 Contains: Reconciliation of GSTR-9 with audited accounts
- 📅 Due Date: 31st Dec of the next financial year
- ✅ Purpose: Ensure books match filed returns
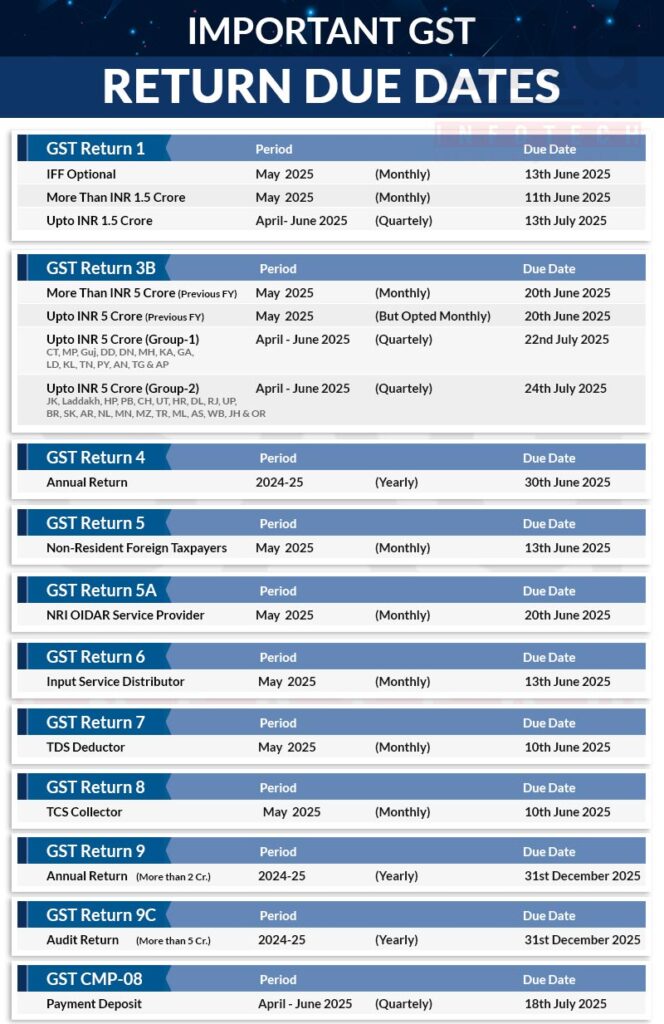
GST Return Filing Due Dates
| Return Type | Frequency | Due Date |
| GSTR-1 | Monthly | 11th of the following month |
| GSTR-3B | Monthly | 20th of the following month |
| GSTR-4 | Annually | 30th April of the following financial year |
| GSTR-5 | Monthly | 20th of the following month |
| GSTR-6 | Monthly | 13th of the following month |
| GSTR-7 | Monthly | 10th of the following month |
| GSTR-8 | Monthly | 10th of the following month |
| GSTR-9 | Annually | 31st December of the following financial year |
| GSTR-9C | Annually | 31st December of the following financial year |
| GSTR-10 | Once | Within 3 months of cancellation/surrender |
| GSTR-11 | Monthly | 28th of the following month |
Note: Due dates may vary based on government notifications.
Penalties for Late Filing of GST Returns
- Late Fee: ₹100 per day under CGST and ₹100 per day under SGST, totaling ₹200 per day. Maximum late fee is ₹5,000.
- Interest: 18% per annum on the outstanding tax amount, calculated from the due date till the actual payment date.
Note: For GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C, late fees and penalties may differ based on turnover and specific conditions.
Tips to Ensure Timely GST Compliance
- Maintain Accurate Records: Regularly update sales and purchase data.
- Set Reminders: Keep track of due dates to avoid penalties.
- Reconcile ITC: Match purchase registers with GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult tax professionals for complex filings.
Other Important Auto-Generated GST Forms
These are not filed manually but help you reconcile and verify data.
GSTR-1A – Amendment of Sales (⛔ Obsolete)
- ❗ Note: This form is no longer in use (was used to accept/reject buyer corrections)
- ✅ Now: Amendments can be done directly in future GSTR-1
GSTR-2A – Auto-Drafted Purchase Data (Dynamic)
- 📌 For: Buyers
- 📄 Contains: Inward supplies from sellers’ GSTR-1, GSTR-5, GSTR-6
- ⚠️ Nature: Changes as seller files or revises data
- ✅ Use: Cross-check but don’t use for final ITC claim
GSTR-2B – Static ITC Statement
- 📌 For: Buyers
- 📄 Contains: ITC available and ineligible, based on supplier filings
- 📅 Available On: 14th of next month
- ✅ Use: Preferred source for ITC claim in GSTR-3B
Quick Tips to Stay Compliant
- 🕒 File on time to avoid late fees & interest
- 🧮 Match GSTR-2B with purchase register before claiming ITC
- 🔄 Regularly reconcile GSTR-1, 3B, 2A, and 2B
- 📢 Update details in GSTR-1 monthly/quarterly for accurate credit to buyers
FAQs
What are GST Returns?
GST Returns are forms that registered taxpayers must file with the government to report their sales, purchases, tax collected, and tax paid under the Goods and Services Tax regime.
Who needs to file GST Returns?
All businesses registered under GST—including regular taxpayers, composition dealers, e-commerce operators, and non-resident taxable persons—are required to file specific GST Returns based on their category and turnover.
What is the due date for filing GSTR-3B?
GSTR-3B is typically due on the 20th of the following month for monthly filers. For quarterly filers under the QRMP scheme, it’s the 22nd or 24th, depending on the state.
What happens if I file GST Returns late?
Late filing attracts a penalty of ₹200 per day (₹100 under CGST and ₹100 under SGST), up to a maximum of ₹5,000. Interest at 18% per annum is also charged on late tax payment.
What is the difference between GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B?
GSTR-1 contains detailed invoice-wise outward supply data, while GSTR-3B is a monthly summary return used to discharge tax liability.
Is GSTR-9 mandatory for all taxpayers?
GSTR-9 is mandatory for regular taxpayers with a turnover exceeding ₹2 crore in a financial year. However, those below this limit may be exempt or have simplified filing requirements.
Can I revise a GST Return after filing?
No, once a GST Return is filed, it cannot be revised. However, you can make corrections or adjustments in the subsequent month’s return.
What is GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B used for?
GSTR-2A is a dynamic, auto-generated report showing inward supplies based on seller filings. GSTR-2B is a static monthly statement used to accurately claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).
What is the penalty for not filing GSTR-9C?
Non-filing of GSTR-9C can lead to a penalty of ₹100 per day under CGST and SGST each, subject to a maximum of 0.25% of the taxpayer’s turnover.
Where can I check my GST Return filing status?
You can check your GST Return filing status by logging into the GST portal and navigating to Returns Dashboard > View Filed Returns.